Unraveling the Iterator Pattern within the World of Behavioral Patterns
At its core, the Behavioral Patterns realm is all about objects behaving nicely together, like a well-rehearsed orchestra. Among these patterns, the Iterator stands out as the gracious maestro, ensuring every instrument (or in our case, object) gets its turn in the spotlight without revealing the intricacies of the orchestra’s arrangement.
The Iterator Pattern, nestled within the Behavioral Patterns family, is like that reliable friend who ensures you never miss a beat in a song or a step in a dance. It simplifies the act of moving through collections, making our coding lives a tad bit easier and a whole lot more elegant. So, the next time you loop through a list, take a moment to tip your hat to the trusty Iterator Pattern working behind the scenes.
- The Essence of the Iterator: Think of the Iterator Pattern like a savvy tour guide of a museum. You want to see every artifact, right? But do you really need to know the intricate layout of the whole museum? Nope. That's where our guide (the Iterator) shines, leading us through each item one by one, ensuring we don’t miss out.
- Why Do We Need It?
Here’s the crux: not all collections (like arrays, lists, trees) store their elements the same way. But if we’re building applications, we often just want to process each item in a collection without getting bogged down by its underlying structure. The Iterator Pattern lets us do just that, traverse a collection seamlessly without exposing its guts. - Breaking Down the Mechanics:
- Iterator Interface: This is the promise every iterator makes. It usually has methods like `next()` to move to the next item, `hasNext()` to check if more items are available, and sometimes `remove()` to eliminate an item on the go.
- Concrete Iterator: This is where the magic happens. Each collection type will have its own version of an iterator, but all adhere to the standard interface.
- Aggregate or Collection: It's the ensemble of items we're looking to traverse. Think of it as our museum. It provides a way to fetch its iterator, but keeps its inner layout hidden.
- The Charm in Simplicity:
The beauty of the Iterator Pattern lies in its elegance. By decoupling the act of iteration from the underlying collection, it offers a uniform way to traverse various data structures. This means whether you're dealing with a simple list or a complex tree, the way you access each item remains consistent. - Where It Fits in the Behavioral Patterns Family:
While many Behavioral Patterns focus on communication between objects (like the Observer Pattern watching over changes, or the Strategy Pattern allowing objects to switch out their behavior), the Iterator is all about access and traversal. It’s the unsung hero ensuring every object in a collection gets its moment, all the while keeping things neat and tidy. - A Modern Take:
If you’ve ever used a `for-each` loop in languages like Java, Python, or C#, you've already danced with the Iterator Pattern. Modern languages often have built-in support for iteration, making it even more intuitive for developers to traverse collections.
The Iterator Pattern, nestled within the Behavioral Patterns family, is like that reliable friend who ensures you never miss a beat in a song or a step in a dance. It simplifies the act of moving through collections, making our coding lives a tad bit easier and a whole lot more elegant. So, the next time you loop through a list, take a moment to tip your hat to the trusty Iterator Pattern working behind the scenes.
Iterator Pattern Description
The iterator pattern provides a consistent way to sequentially access items in a collection that is independent of and separate from the underlying collection. The figure below represents the iterator pattern.
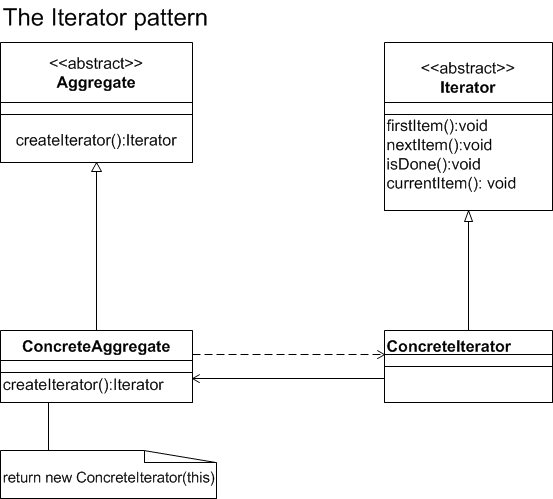
Benefits of using the Iterator Pattern:
- Supports variations in the traversal of a collection
- Simplifies the interface of the collection.
When to Use the Iterator Pattern:
You should use the Interpreter pattern when you want to:
- Access a collection object’s contents without exposing its internal representation.
- Support multiple traversals of objects in a collection.
- Provide a uniform interface for traversing different structures in a collection.
In object-oriented programming, the iterator pattern is a design pattern in which an iterator is used to traverse a container and access the container's elements. The iterator pattern decouples algorithms from containers; in some cases, algorithms are necessarily container-specific and cannot be decoupled. For example, the hypothetical algorithm SearchForElement can be implemented generally using a specified type of iterator rather than implementing it as a container-specific algorithm. This allows SearchForElement to be used on any container that supports the required type of iterator.
Iterator Pattern in Java